
Thermoforming
We shape plastics to perfection.
Thermoforming is primarily used for prototypes and small production runs because it is cost-efficient, flexible, and fast compared to other plastic forming processes. It is particularly suitable for complex geometries or large-area components and serves as a proven alternative to injection molding or CNC milling.
Maximum data protection
Your data is in safe hands with us
35 years of experience
Resilient prototypes for your projects
Efficiency
Combination of versatility and material diversity
For every industry
From automotive to dentistry
Well advised
Reach your goal quickly with our experts
Maximum data protection
Your data is in safe hands with us
35 years of experience
Resilient prototypes for your projects
Efficiency
Combination of versatility and material diversity
For every industry
From automotive to dentistry
Well advised
Reach your goal quickly with our experts
Functionality of the Thermoforming Process.
The thermoforming process is based on the controlled heating of a plastic sheet, which is then drawn over a shaping contour. The material precisely adapts to the mold and is subsequently fixed by cooling.
Heating
The plastic sheet is clamped into a holder and heated to the optimal processing temperature. This is done using infrared heaters, convection ovens, or contact heating systems. Uniform temperature distribution is crucial to avoid stress or material defects. Depending on the material, the temperature varies to ensure ideal formability.
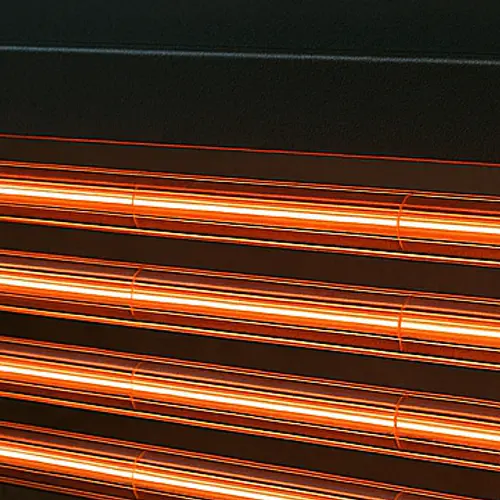

The clamped plastic sheet is heated by infrared heaters.
Forming
The heated plastic sheet is formed over or into a mold using vacuum or mechanical pressure. The forming process is fast and highly precise. Two methods can be used: Vacuum forming, where the material is drawn over the mold by negative pressure, or pressure forming, which combines vacuum with compressed air to achieve better material distribution and greater detail accuracy.

Positive thermoformed parts.
Cooling
The formed part is carefully cooled to stabilize its final shape. Cooling is typically done using air or water. Once solidified, the component is removed from the mold.
Formed plastic part in the forming tool
Demolding
The finished part is removed from the mold and may undergo post-processing. To achieve precise contours and the desired surface finish, the thermoformed parts undergo post-processing steps such as milling, cutting, painting, printing, or the application of protective coatings. These finishing processes ensure that the components are tailored to their specific application and optimized for use in prototypes and small production runs.

Surface detail of a painted thermoformed piece.
Typical Application Areas
Thermoforming is used in various industries, particularly where complex, lightweight, and stable components are required.
Mechanical Engineering
Housings, covers, and technical components that require high stability with minimal weight.
Automobilindustrie
Interior trims, trunk components, load compartment covers, air ducts, and functional parts
Medical Technology
Protective covers and packaging for sensitive devices and instruments
Electronics Industry
Precisely fitting housings for electrical components and assemblies
Packaging Technology
Thermoformed plastic packaging for products requiring special protection or a specific shape.
Advantages of thermoforming for prototypes and small series
Thermoforming offers significant advantages, particularly for the production of prototypes and small series. Compared to other forming processes, it is cost-effective, flexible, and quick to implement.
- Cost efficiency for small production runs
Unlike injection molding, which requires expensive metal molds, the tooling costs for thermoforming are significantly lower. This makes the process especially attractive for small to medium production runs, as it eliminates the need for high investments in complex mold tools.
- Fast production and development times
Thermoforming tools can be produced and modified in a short time, making prototypes quickly available. This is particularly beneficial in product development, where designs need to be tested or optimized.
- High design flexibility and shape variety
The thermoforming process allows the production of large, deep, and complex-shaped components with uniform wall thickness. Compared to CNC milling, material usage is more efficient, as less waste is generated.
- Material and weight reduction
By using thin-walled plastic sheets, lightweight yet stable components can be manufactured. This makes thermoforming ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial, such as in mechanical engineering or medical technology.
- Flexibility for custom adaptations
Design changes or customer-specific modifications can be quickly implemented, as tools can be easily modified or newly produced. This is a major advantage for companies that require customized solutions in small quantities.
Thanks to these advantages, thermoforming is an efficient and cost-effective solution for prototypes and small series, especially when fast development cycles and flexible production options are required.
Our case studies
Automotive
A body with class: We produced the master model for the body of the cult Evetta light electric vehicle on a 1:1 scale – with perfect milling and the finest surface finishing. Find out how.
Industry
The socket for the forest: We developed the prototypes for a type of powerbank for Stihl, which was put through its paces by forestry workers. A truly powerful project.
Aerospace
"Jena, we have no problem": Jena-Optronik commissioned MODELLTECHNIK to produce a 1:1 model of the Gateway Docking Port, which is needed for sensor tests in space applications.
Design
Timeless and dignified: Working with Samosa and our expertise in 3D printing, MODELLTECHNIK creates beautiful templates and design samples for individually designed funeral urns.
Contact us
Whether you’ve got technical, commercial or specialist questions – we’re here to help.
START A QUERY NOW„Spot-on delivery under extreme time pressure [...] It couldn't be more perfect“
„Spot-on delivery under extreme time pressure [...] It couldn't be more perfect“